The Underground Hydrogen Storage Market is rapidly gaining importance as countries invest in cleaner and more resilient energy systems. As hydrogen becomes a key pillar of the global energy transition, the challenge of storing it safely and efficiently at scale has come to the forefront. Underground hydrogen storage (UHS) presents a reliable and cost-effective solution by utilizing natural geological formations such as salt caverns, depleted oil and gas reservoirs, and aquifers to store large quantities of hydrogen for extended periods. This storage method supports grid flexibility, energy security, and industrial decarbonization, making it a crucial component in building a sustainable hydrogen economy.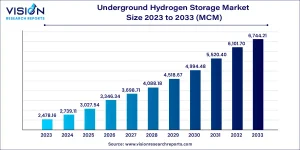
Underground Hydrogen Storage Market Overview
The underground hydrogen storage market is emerging as a vital component of the global energy transition. With renewable energy sources like solar and wind generating electricity intermittently, storing surplus energy as hydrogen and later retrieving it when needed is becoming a practical and scalable solution. Underground storage offers cost efficiency, high storage capacity, and energy security, making it ideal for industrial and utility-scale applications.
Get a Sample@ https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/sample/41619
Underground Hydrogen Storage Market Growth
The demand for underground hydrogen storage is accelerating due to the rapid development of green hydrogen infrastructure worldwide. Countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and the United States are investing heavily in hydrogen strategies and pilot projects. This growth is further supported by international climate targets, which encourage low-carbon technologies to decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors such as steel, chemicals, and transport.
In addition, as hydrogen becomes a globally traded commodity, the need for regional storage hubs is increasing. Underground storage ensures supply stability by acting as a buffer during fluctuations in production and consumption. This growth trajectory is expected to continue as governments roll out roadmaps and funding mechanisms for hydrogen ecosystems.
Underground Hydrogen Storage Market Trends
- Geological Advancements: Recent breakthroughs in subsurface mapping, 3D geological modeling, and reservoir simulation are transforming how underground hydrogen storage sites are selected and developed. These tools allow engineers to evaluate the safety, capacity, and performance of geological formations with higher accuracy. Technologies like seismic imaging and geochemical modeling also help assess hydrogen reactivity with surrounding rock and materials, reducing the risk of leakage and improving long-term storage reliability.
- Green Hydrogen Integration: Underground hydrogen storage is becoming increasingly integrated with green hydrogen production, where hydrogen is produced through water electrolysis powered by renewable sources like solar and wind. By linking storage directly to clean production facilities, energy providers can store excess green hydrogen during high generation periods and deploy it when demand rises. This not only supports a low-carbon energy cycle but also enhances the economics and scalability of renewable hydrogen projects.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Governments are joining forces with energy companies, technology developers, and research institutions to co-fund and pilot underground hydrogen storage projects. These partnerships are accelerating innovation and helping build regulatory frameworks. Initiatives in Europe (like the HyUnder and Hystock projects) and the U.S. (through the Department of Energy’s HyBlend program) are helping validate storage technologies and prepare them for commercial deployment.
- Repurposing Oil and Gas Infrastructure: One growing trend is the reuse of depleted oil and gas reservoirs for hydrogen storage. These formations already have the structural characteristics needed for containment, along with existing pipelines and monitoring systems. Repurposing such infrastructure lowers capital investment and speeds up development, making the transition from fossil fuels to clean energy more cost-effective.
Supporting Green Hydrogen Production
Underground hydrogen storage is a foundational element in scaling green hydrogen initiatives. As electrolysis plants generate hydrogen using renewable energy, production often exceeds immediate demand—especially during peak solar or wind periods. By storing the excess hydrogen underground, producers can balance supply with consumption needs, ensuring steady availability even when weather conditions are unfavorable. This stabilizes the hydrogen supply chain, lowers energy curtailment, and supports the development of a continuous, 24/7 clean energy system for industries like power, chemicals, and transportation.
Backup for Emergency Energy Supply
In times of grid instability, natural disasters, or unexpected energy shortages, hydrogen stored underground can be rapidly deployed as a clean backup power source. Through fuel cells or gas turbines, it can be converted back into electricity almost instantly. This makes it an ideal emergency solution for critical infrastructure like hospitals, military bases, data centers, and water treatment plants. Unlike batteries, which have limited duration, hydrogen can provide power for longer periods, offering a more reliable and scalable alternative in crisis scenarios.
Fuel for Space and Aviation
Hydrogen is already widely used in the aerospace industry as rocket fuel due to its high energy density and clean combustion. With the rise of hydrogen-powered aircraft and innovations in aviation fuel technologies, underground hydrogen storage ensures that large, high-purity reserves are readily available for fueling operations. As global air travel transitions to more sustainable solutions, secure hydrogen storage will be crucial in powering both orbital missions and next-generation commercial aircraft, especially at strategic aerospace hubs and spaceports.
Community and Microgrid Energy Systems
For rural or remote communities with limited access to traditional power infrastructure, underground hydrogen storage offers a transformative solution. When coupled with renewable generation and local electrolysis, hydrogen can be stored underground and converted back to electricity for homes, farms, schools, and health clinics. These community-based microgrids become self-sufficient, resilient, and clean, reducing dependence on costly diesel fuel and improving energy equity. It also opens new pathways for rural electrification and sustainable agriculture in developing regions.
Integrating with Carbon Capture and Utilization
In blue hydrogen production, natural gas is used as a feedstock, and the CO₂ generated is captured and stored underground via carbon capture and storage (CCS). Some underground sites are being designed to accommodate both hydrogen and CO₂, maximizing the value of the geological formation. This integration not only supports decarbonized hydrogen production but also reduces the cost per ton of storage by using shared infrastructure. It enables industries to meet stricter emission standards while maintaining energy efficiency and supply continuity.
Underground Hydrogen Storage Market Dynamics
Drivers
- Growing demand for renewable energy storage solutions: As countries scale up solar and wind energy, the need for efficient and large-scale energy storage is rising. Underground hydrogen storage offers a reliable way to store surplus renewable power, enabling grid stability and long-term energy supply.
- Increasing investments in hydrogen infrastructure and decarbonization policies: Governments and private sectors are heavily investing in hydrogen technologies as part of their climate change mitigation strategies. These policies promote the development of hydrogen ecosystems, including storage, making underground storage a strategic focus.
Opportunities
- Development of hydrogen storage clusters across Europe and North America: Regions like the EU and U.S. are planning hydrogen storage hubs that link production, storage, and distribution. These integrated clusters create economies of scale and support long-term hydrogen deployment.
- Commercialization of salt cavern storage in emerging markets: Salt caverns offer high purity and quick response times for hydrogen storage. Emerging markets with suitable geological formations can benefit from low-cost, scalable solutions as technology becomes more accessible.
Challenges
- High upfront costs of infrastructure and geological site development: Initial capital investment required for site preparation, safety systems, and hydrogen handling infrastructure is substantial. This often delays project execution without strong financial incentives or support.
- Lack of standardized regulations and certification across countries: The global hydrogen market is still developing, and inconsistent safety standards, testing protocols, and certification procedures hinder cross-border collaboration and scalability of underground storage projects.
- Supporting Green Hydrogen Production: Underground hydrogen storage is a key enabler for large-scale green hydrogen projects. It allows producers to store hydrogen generated via electrolysis from renewable energy, ensuring that the hydrogen is available even when production pauses. This smooths out fluctuations in renewable power and makes green hydrogen supply more predictable and scalable for industrial and commercial use.
Backup for Emergency Energy Supply
In times of power grid failure or extreme weather, stored hydrogen acts as a critical backup. It can be converted into electricity through fuel cells or turbines, offering fast and clean emergency energy. This makes underground hydrogen storage a valuable tool for enhancing disaster preparedness and grid resilience in energy-sensitive regions.
- Fuel for Space and Aviation: Hydrogen is a crucial component in aerospace and future aviation. As interest grows in hydrogen-powered aircraft and rockets, underground storage offers a way to maintain large, secure hydrogen reserves that meet the strict demands of these high-performance sectors.
- Community and Microgrid Energy Systems: In remote or off-grid locations, underground hydrogen storage supports local microgrids that depend on solar and wind. These systems can store hydrogen locally to ensure round-the-clock clean power for rural homes, small businesses, and even farming operations reducing reliance on diesel generators or unstable power lines.
- Integrating with Carbon Capture and Utilization: Some underground hydrogen projects are linked to carbon capture and storage (CCS) facilities. This integration helps industries produce blue hydrogen, where emissions from hydrogen production are captured and stored underground. This dual use of geological formations increases economic efficiency and reduces environmental impact.
Applications in the Market
Underground hydrogen storage plays a vital role in grid balancing by storing excess electricity generated from renewable sources like solar and wind. This stored hydrogen can be converted back into power during periods of low generation, helping to stabilize the electricity grid and maintain supply-demand equilibrium.
In the industrial sector, stored hydrogen serves as a critical feedstock for various processes, including oil refining, ammonia production, and steel manufacturing. Its availability in large quantities through underground storage ensures consistent supply for energy-intensive operations.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between energy companies, research institutes, and governments is fueling pilot projects and regulatory frameworks to accelerate commercialization.
- Decentralized Energy Grids: Underground hydrogen storage supports the development of distributed energy systems by acting as a long-term backup for off-grid and microgrid setups.
Case Study: HyStock Project – The Netherlands
The HyStock project, led by Gasunie, is a pioneering underground hydrogen storage initiative in Veendam, Netherlands. It aims to store green hydrogen in salt caverns and serve as a key hub for the Dutch and European hydrogen network. The project showcases the feasibility of UHS in supporting energy transition goals and is backed by public and private funding.
Read More:https://www.heathcareinsights.com/europe-polyurethane-market/
Top Manufactures in Underground Hydrogen Storage Market
- Air Liquide
- Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.
- Engie
- Linde plc
- Texas Brine Company, LLC
- Uniper SE
- WSP
Want custom data? Click here:https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/customization/41619
Underground Hydrogen Storage Market Segmentation
By Storage Type
- Porous Media Storage
- Salt Caverns
- Engineered Cavities
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Future Outlook
The future of the underground hydrogen storage market is highly promising. As hydrogen becomes an integral part of global energy systems, storage infrastructure will become critical for ensuring scalability and reliability. Breakthroughs in hydrogen compression, pipeline integration, and geologic modeling will reduce costs and expand site availability. Furthermore, international policy alignment and carbon credit incentives are likely to propel investments in this domain.
Buy this Premium Research Report@https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/checkout/41619
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact
sales@visionresearchreports.com| +1 650-460-3308
