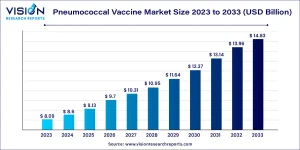
The global pneumococcal vaccine market stood at around USD 8.6 billion in 2024 and is forecast to exceed USD 14.83 billion by 2033, advancing at a CAGR of 6.25% between 2024 and 2033.
Pneumococcal Vaccine Market Overview
The pneumococcal vaccine market is an essential segment of the global healthcare industry, driven by the growing awareness of pneumococcal diseases and their associated health risks. Pneumococcal vaccines protect against infections caused by the Streptococcus pneumoniae bacterium, which can lead to pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. These vaccines are critical in preventing severe infections, especially among children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. The increasing focus on immunization programs and preventive healthcare has further reinforced the importance of pneumococcal vaccines in public health initiatives worldwide.
Access Your Sample Report Today: https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/sample/41294
Pneumococcal Vaccine Market Growth
The pneumococcal vaccine market is witnessing steady growth due to the rising global prevalence of pneumococcal diseases and increased government initiatives to enhance vaccination coverage. Growing investments by pharmaceutical companies in research and development are introducing newer conjugate and polysaccharide vaccines with broader serotype coverage, improving effectiveness across diverse populations.
Another factor contributing to market growth is the rising awareness among parents and healthcare providers regarding the benefits of routine vaccination schedules. Immunization campaigns, coupled with partnerships between governments and private organizations, are expanding access to vaccines in both developed and developing regions, supporting widespread adoption.
What is the Importance of Using a Pneumococcal Vaccine?
The pneumococcal vaccine plays a crucial role in protecting people against Streptococcus pneumoniae, a bacterium responsible for serious and potentially life-threatening illnesses. These infections include pneumonia (a lung infection), meningitis (infection of the brain and spinal cord lining), and sepsis (a severe bloodstream infection). Left untreated, such conditions can lead to long hospital stays, long-term health problems, or even death, particularly among vulnerable populations.
Children under the age of two, older adults above 65, and individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions are at the highest risk of developing severe complications. Vaccination provides these groups with a shield of protection, helping to reduce both personal risk and the spread of the infection within communities.
Beyond individual protection, the vaccine contributes to herd immunity, lowering the overall transmission rate of pneumococcal diseases. This benefits society by reducing healthcare costs, hospitalizations, and the use of antibiotics, which in turn helps fight the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. In many countries, the inclusion of pneumococcal vaccines in national immunization programs has drastically lowered disease incidence, proving its importance as a cornerstone of modern preventive healthcare.
How to Use a Pneumococcal Vaccine?
The pneumococcal vaccine is administered as an injection, usually in the upper arm for adults and in the thigh for infants and young children. The dosage and schedule depend on the age of the individual and their health condition.
- Infants and Children: The vaccine is often part of routine childhood immunization programs. Typically, multiple doses are given in the first two years of life, starting as early as two months of age. This ensures early protection when children are most vulnerable.
- Adults and Elderly: For adults over 65 years old, as well as those with chronic illnesses such as diabetes, lung disease, or heart disease, a single dose or a booster dose may be recommended. Healthcare providers decide based on the patient’s overall health and vaccination history.
- High-Risk Groups: People with compromised immune systems (such as cancer patients, organ transplant recipients, or individuals with HIV) may require additional doses for stronger protection.
The vaccination schedule is carefully designed by healthcare providers to suit individual needs. Since there are two main types of pneumococcal vaccines conjugate vaccines (PCV) and polysaccharide vaccines (PPSV) sometimes both are given at different intervals to ensure broader protection.
How Effective is the Pneumococcal Vaccine?
The pneumococcal vaccine has been proven to be highly effective in preventing severe and invasive pneumococcal diseases. In children, conjugate vaccines (PCV13, PCV15, etc.) provide long-lasting immunity and significantly reduce the risk of infections like meningitis and bacteremia. Countries that have introduced PCV into their childhood immunization programs have reported dramatic declines in pneumococcal-related hospital admissions and deaths.
For adults, especially those aged 65 and older, the vaccine lowers the risk of pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and serious complications that can result in hospitalization. Even though the vaccine does not guarantee complete protection no vaccine does it greatly reduces the severity of illness in those who do contract the infection. This often means fewer hospital stays, faster recovery, and a reduced risk of life-threatening outcomes.
Pneumococcal Vaccine Market Dynamics
Drivers
The pneumococcal vaccine market is primarily driven by the rising prevalence of pneumococcal diseases and the recognition of their serious health consequences. Increasing government initiatives, funding for immunization programs, and campaigns to raise public awareness are further boosting vaccine demand. Advances in vaccine technology and research also contribute to market growth by providing more effective and broader protection.
Opportunities
Significant opportunities exist in emerging markets where vaccination coverage remains low. Development of next-generation vaccines, such as broader conjugate vaccines and combination formulations, can open new revenue streams. Collaborations with international organizations and public health agencies can help reduce costs, improve distribution networks, and expand access in underserved areas. Additionally, digital health platforms present opportunities for enhancing vaccine awareness and education.
Challenges
The market faces several challenges that may restrict growth. High production and distribution costs make vaccines less accessible in low-income regions. Regulatory compliance requirements and lengthy approval processes can delay the introduction of new vaccines. Logistical challenges, such as maintaining cold-chain storage in remote or rural areas, add complexity. Vaccine hesitancy fueled by misinformation and cultural factors also poses a significant barrier to widespread immunization.
Want custom data? Click here: https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/customization/41294
Pneumococcal Vaccine Market Trends
- Expansion of Pediatric Immunization Programs: Many countries are incorporating pneumococcal vaccines into their national immunization schedules, significantly increasing coverage among infants and young children. Governments are also running awareness campaigns to educate parents about the importance of early vaccination.
- Innovative Vaccine Development: Pharmaceutical companies are actively developing next-generation vaccines with broader serotype coverage, enhanced immune response, and longer-lasting protection. Research is also exploring combination vaccines to simplify immunization schedules.
- Public-Private Collaborations: Strategic partnerships between governments, NGOs, and vaccine manufacturers are enabling more affordable and widespread vaccine distribution. Such collaborations also focus on strengthening supply chains in low-income and underserved regions.
- Digital Health and Awareness Campaigns: Digital platforms, mobile apps, and social media campaigns are increasing public knowledge about pneumococcal diseases. These efforts drive higher vaccine acceptance rates, especially among younger, tech-savvy parents.
- Focus on Adult and Geriatric Vaccination: Beyond pediatric immunization, there is growing emphasis on vaccinating adults and elderly populations due to higher susceptibility to pneumococcal infections. Healthcare providers are recommending routine vaccinations to prevent serious complications.
Case Study
One of the most impactful examples of pneumococcal vaccine implementation is seen in Southeast Asia, where several countries have introduced the vaccine into their national immunization programs. By focusing on vaccinating infants, young children, and high-risk adults, these programs have led to a measurable decline in invasive pneumococcal diseases such as meningitis and bacteremia. The success was made possible through strategic partnerships between governments, global health organizations like Gavi and WHO, and leading vaccine manufacturers. These collaborations not only ensured affordable pricing but also strengthened cold-chain systems to reach remote areas.
Read More: https://www.heathcareinsights.com/cell-processing-instruments-market/
Pneumococcal Vaccine Market Key Players
- Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd.
- CSL
- Sanofi
- GSK plc
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Walvax Biotechnology Co., Ltd
- Beijing Minhai Biotechnology Co.,Ltd (Subsidiary of Shenzhen Kangtai Biological Products Co.
- Ltd.)
Pneumococcal Vaccine Market Segmentations
By Vaccine Type
- Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
- Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine
By Product
- Prevnar 13
- Synflorix
- Pneumovax 23
- VAXNEUVANCE
- PNEUMOSIL
- Other Products
By End-use
- Public Sector
- Private Sector
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)
Future Outlook
The pneumococcal vaccine market is expected to maintain steady growth in the coming years, driven by rising healthcare investments, continuous innovation, and stronger policy support. Advancements in biotechnology are leading to the development of next-generation vaccines that cover more pneumococcal serotypes and offer longer-lasting protection. Combination vaccines, which include pneumococcal protection along with other childhood immunizations, are likely to simplify schedules and improve compliance among parents and healthcare providers.
Another key factor shaping the future is the expansion of vaccination programs into low- and middle-income countries, supported by international health alliances. As healthcare infrastructure strengthens and awareness increases, vaccination rates are expected to rise significantly in regions that previously had limited access.
Buy this Premium Research Report@ https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/checkout/41294
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact
sales@visionresearchreports.com| +1 650-460-3308
