The U.S. point-of-care glucose testing market was valued at approximately USD 1.18 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach around USD 1.84 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.53% between 2024 and 2033.
The U.S. point-of-care glucose testing market is primarily driven by the rising prevalence of diabetes and the increasing need for rapid, accurate glucose monitoring in hospitals, emergency care, and home settings. Technological advancements in smart meters, biosensors, and connected devices are enhancing usability and accuracy, while growing patient awareness and preference for convenient, home-based testing are further fueling market adoption.
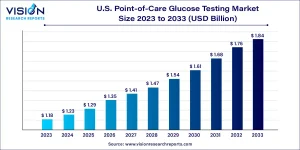
U.S. Point-of-Care Glucose Testing Market Overview
The U.S. point-of-care glucose testing market is a critical component of diabetes management and overall healthcare diagnostics. Point-of-care glucose tests provide rapid and accurate blood sugar readings, enabling timely clinical decisions for both acute and chronic care settings. Increasing prevalence of diabetes, growing awareness of self-monitoring, and advancements in portable and connected devices have significantly influenced the adoption of POC glucose testing solutions across hospitals, clinics, and home-care environments.
Access Your Sample Report Today: https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/sample/41323
U.S. Point-of-Care Glucose Testing Market Growth
The market has witnessed robust growth driven by technological innovations in glucose monitoring devices. Modern POC glucose meters are increasingly compact, user-friendly, and integrated with digital health platforms, providing real-time data to patients and healthcare providers. This has enhanced the accuracy and convenience of monitoring, resulting in better glycemic control and improved patient outcomes.
In addition, healthcare providers are emphasizing early diagnosis and continuous monitoring to reduce diabetes-related complications. The increasing number of clinical initiatives, patient education programs, and government-backed healthcare campaigns has further accelerated market expansion. Integration of POC glucose testing with telemedicine platforms is also emerging as a major growth avenue, allowing remote monitoring and real-time clinical interventions.
U.S. Point-of-Care Glucose Testing Market Trends
- Technological Advancements in Devices: Adoption of non-invasive and minimally invasive glucose testing devices is accelerating, providing pain-free, faster, and more accurate readings. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are gaining popularity for real-time tracking and better long-term glycemic control.
- Integration with Digital Health Platforms: Modern glucose meters are increasingly linked with mobile applications, cloud platforms, and electronic health records. This integration allows real-time tracking, personalized health insights, remote monitoring by clinicians, and improved patient engagement in diabetes management.
- Rising Home-Based Testing: The growing preference for home monitoring is driving demand for portable, easy-to-use devices. Home-based testing reduces hospital visits, empowers patients to manage their conditions independently, and improves adherence to treatment plans.
- Focus on Accuracy and Speed: With healthcare providers prioritizing patient safety, devices that deliver rapid, precise, and reliable results are in high demand. Accurate readings are crucial for preventing hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic episodes, especially in critical care and emergency settings.
- Wearable and Continuous Monitoring Devices: The trend toward wearable devices, such as smart patches and sensors, allows continuous glucose monitoring without frequent finger pricks. This technology supports proactive disease management and alerts patients to abnormal glucose fluctuations in real time.
- Telemedicine Integration: The rise of telehealth is encouraging the adoption of connected glucose testing devices. Patients can share readings remotely with healthcare providers, enabling timely adjustments in therapy and reducing the need for in-person consultations.
Major Advantages and Disadvantages of Point-of-Care Testing (POCT)
Advantages
- Rapid Results: POCT provides immediate diagnostic readings, often within minutes, allowing healthcare providers to make timely clinical decisions. This is particularly crucial in emergency settings, critical care, and perioperative monitoring, where delays in laboratory results can affect patient outcomes.
- Convenience: These tests can be performed directly at the patient’s bedside, in outpatient clinics, or at home, reducing the need for hospital visits and laboratory dependency. This convenience improves workflow efficiency for healthcare providers and enhances access to healthcare for patients with mobility or transportation limitations.
- Improved Patient Engagement: POCT empowers patients to take an active role in managing their health. By monitoring blood glucose or other parameters in real time, patients can better understand the impact of diet, medication, and lifestyle choices, leading to improved adherence to treatment plans and overall disease management.
- Enhanced Clinical Workflow: By providing immediate results, POCT reduces the turnaround time compared to centralized laboratory testing. This streamlines decision-making, accelerates treatment initiation, and can improve overall hospital efficiency.
- Early Detection of Complications: Regular monitoring at the point of care allows clinicians to detect abnormal trends or critical values quickly, reducing the risk of severe complications and hospital readmissions.
Disadvantages
- Accuracy Variability: While convenient, POCT devices may have lower precision compared to central laboratory analyzers. Factors such as calibration errors, environmental conditions, or device quality can affect the reliability of results.
- User Errors: Improper sample collection, incorrect use of devices, or failure to follow procedural guidelines can compromise results, especially in home-based or minimally supervised settings.
- Cost Considerations: Repeated testing requires consumables like test strips, lancets, and sensors, which can become costly over time. Some devices also have high upfront costs, which may limit accessibility.
- Limited Test Range: While POCT is excellent for specific tests like glucose or cardiac markers, it may not replace comprehensive laboratory evaluations for complex diagnostics, requiring complementary lab tests for confirmation.
Different Types of Point-of-Care Testing
POCT includes a wide array of tests that provide immediate, actionable insights across multiple clinical areas:
- Blood Glucose Testing: Includes traditional glucometers, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, and emerging non-invasive devices. These tests are vital for diabetes management, acute care, and monitoring metabolic health.
- Cardiac Markers: Rapid testing for troponin, BNP, and CK-MB helps in the immediate evaluation of cardiac events like heart attacks or heart failure, supporting urgent clinical interventions.
- Hematology Tests: Quick assessments of hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet counts are used in anemia diagnosis, bleeding disorders, and preoperative evaluations, enabling immediate clinical responses.
- Infectious Disease Testing: Rapid diagnostics for influenza, COVID-19, HIV, streptococcal infections, and other pathogens allow timely isolation, treatment, and public health interventions, particularly in outpatient or remote settings.
- Coagulation Testing: INR and PT tests are critical for monitoring patients on anticoagulant therapy, ensuring safe dosing and preventing excessive bleeding or clotting.
- Urinalysis: Point-of-care urinalysis detects proteins, glucose, ketones, and other markers for renal and metabolic disorders. Quick results aid in early diagnosis and continuous monitoring.
- Other Emerging POCT Applications: New tests are being developed for liver function, lipid profiles, electrolyte monitoring, and hormone levels. These expansions are enhancing the versatility of POCT in routine and critical care.
Critical Values for Point-of-Care Testing
Critical values in point-of-care testing (POCT) are thresholds that indicate potentially life-threatening conditions, requiring immediate clinical attention or intervention. Recognizing these values ensures timely treatment, prevents complications, and improves patient outcomes.
- Blood Glucose Critical Values: Hypoglycemia: Blood glucose levels below 54 mg/dL are considered critically low. Immediate intervention, such as administration of glucose or glucagon, is essential to prevent seizures, loss of consciousness, or other severe complications.
- Hyperglycemia: Levels above 400 mg/dL can signal conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), both of which require urgent medical attention. Prompt management with fluids, insulin therapy, and electrolyte monitoring is critical.
- Other POCT Parameters: Cardiac Markers: Elevated troponin levels indicate myocardial infarction or acute cardiac events, necessitating rapid intervention to restore heart function and prevent permanent damage.
- Coagulation Tests: An International Normalized Ratio (INR) above 5 signals a high risk of bleeding in patients on anticoagulant therapy and requires immediate adjustment of medication.
- Hematology: Extremely low hemoglobin or platelet counts can indicate acute anemia or bleeding disorders, demanding urgent transfusions or treatment.
- Infectious Disease Markers: Rapid detection of pathogens such as influenza, COVID-19, or bacterial infections at critical thresholds enables timely isolation, treatment, and infection control measures.
U.S. Point-of-Care Glucose Testing Market Dynamics
Drivers
The U.S. point-of-care glucose testing market is experiencing strong growth due to several key drivers. The rising prevalence of diabetes, including type 1 and type 2, has created a consistent demand for rapid and accurate glucose monitoring. Hospitals, emergency care units, and outpatient clinics require timely readings to make critical treatment decisions. Increasing consumer preference for convenient, home-based glucose testing is also fueling adoption, as patients seek more control over their health. Additionally, continuous technological innovations in biosensors, smart meters, wearable devices, and connected monitoring systems are enhancing usability, accuracy, and accessibility, further driving market expansion.
Opportunities
Emerging technologies and digital health integration present significant growth opportunities. The incorporation of AI and IoT in glucose monitoring enables predictive analytics, early detection of abnormal glucose trends, and personalized treatment recommendations. Telemedicine adoption is creating new channels for remote patient monitoring, reducing hospital visits and enhancing chronic disease management. Moreover, there is substantial potential in the development of non-invasive and minimally invasive glucose monitoring devices, which can improve patient compliance, comfort, and long-term adherence. Partnerships between device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and tech companies are also expanding market reach and fostering innovation.
Challenges
Despite promising growth, the market faces notable challenges. High device and consumable costs, such as test strips and sensors, may limit accessibility for some patient populations. Regulatory approvals and compliance with healthcare standards can be complex and time-consuming, slowing product launches. Concerns over data privacy, cybersecurity, and integration with electronic health records can impede adoption, particularly for connected devices. User errors during self-testing, lack of proper training, and limited awareness in certain demographic groups may compromise the accuracy and reliability of results, presenting hurdles to optimal utilization.
Want custom data? Click here: https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/customization/41323
Case Study: Leveraging Continuous Glucose Monitoring in a U.S. Hospital Network
A leading hospital network in the United States successfully implemented a comprehensive diabetes management program by integrating continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems with their electronic health record (EHR) platform. This integration allowed clinicians to access real-time glucose readings for their patients, enabling rapid adjustments to insulin therapy, dietary plans, and other interventions. Over the course of one year, the hospital observed significant improvements in patient outcomes. Patients became more engaged in self-management due to instant feedback and actionable insights, while real-time alerts helped clinicians prevent hypoglycemic events, enhancing overall safety. The proactive monitoring approach also contributed to a reduction in hospital readmissions related to diabetes complications. Additionally, clinicians benefited from enhanced workflow efficiency, as they were able to make faster, data-driven decisions that optimized resource allocation and improved the quality of care.
Read More: https://www.heathcareinsights.com/portable-ultrasound-bladder-scanner-market/
U.S. Point-of-Care Glucose Testing Market Key Players
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Abbott
- Nipro
- Platinum Equity Advisors, LLC (Lifescan, Inc.)
- Nova Biomedical
- ACON Laboratories
- Trividia Health, Inc.
- Prodigy Diabetes Care, LLC
- Bayer AG/Ascensia Diabetes Care Holdings AG
- EKF Diagnostics
U.S. Point-of-Care Glucose Testing Market Segmentation
By Product
- Accu Check Aviva Meter
- Onetouch Verio Flex
- i-STAT
- Freestyle Lite
- Bayer CONTOUR Blood Glucose Monitoring System
- True Metrix
- Accu-Chek Inform II
- StatStrip
- Others
Future Outlook: The Growing Role of POC Glucose Testing in U.S. Healthcare
The U.S. point-of-care glucose testing market is set to experience substantial growth, driven by ongoing technological innovation, integration with digital health platforms, and rising awareness of proactive healthcare. Advancements in non-invasive and minimally invasive sensors, along with wearable devices, are enabling pain-free, continuous monitoring, which enhances patient comfort and adherence.
The incorporation of artificial intelligence and predictive analytics is allowing clinicians to anticipate glucose fluctuations and deliver personalized treatment plans, improving overall disease management. Expansion of telemedicine and remote monitoring services further supports real-time interventions without requiring frequent hospital visits, making care more accessible. Additionally, an increasing focus on preventive healthcare is encouraging the adoption of POC glucose testing in both clinical and home settings. Strategic collaborations between device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and technology companies are fostering innovation, improving device interoperability, and broadening market reach. Collectively, these trends position POC glucose testing as a central component of a patient-centric, technologically advanced diabetes care ecosystem.
Buy this Premium Research Report@ https://www.visionresearchreports.com/report/checkout/41323
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact
sales@visionresearchreports.com| +1 650-460-3308
